What is Sarcopenia?
Sarcopenia is a progressive condition characterized by the gradual loss of muscle mass and strength that typically begins around age 30 and accelerates after 60. Recognizing its early signs can help you take proactive steps to reduce its impact.
The effects of sarcopenia extend beyond reduced muscle size. It also impairs muscle function, leading to decreased strength, balance, and coordination. This increases the risk of falls and fractures, which are common and serious concerns for older adults. In some cases, unintentional weight loss may accompany muscle deterioration, further compounding health risks. Understanding sarcopenia highlights the importance of addressing it early.
Causes of Sarcopenia
One of the primary factors is the natural aging process, which leads to a decline in the number of muscle fibers. However, other significant contributors include lifestyle choices and hormonal changes. Lack of physical activity results in muscle disuse, which accelerates muscle loss. Resistance training, in particular, has been shown to be highly effective in preserving muscle mass and strength.

Lack of exercise and hormonal changes are key contributors. Chronic nutritional deficiencies may also influence muscle health, especially when combined with inactivity.
Symptoms and Signs of Sarcopenia
The most noticeable sign is a decrease in muscle size, which may be accompanied by a loss of strength and endurance. You might find it more challenging to perform everyday tasks, such as climbing stairs, lifting objects, or even standing up from a chair. Conditions like diabetes can exacerbate these symptoms, making it even more important to monitor muscle health and maintain an active lifestyle.
Another common symptom of sarcopenia is reduced balance and coordination. You may experience unsteadiness while walking or a tendency to trip over small obstacles. This can lead to a higher risk of falls, which is a significant concern for older adults.
As sarcopenia progresses, you may notice an overall decline in your physical performance. This can manifest as increased fatigue during activities that were once easy or a longer recovery time after exertion. Additionally, sarcopenia is often associated with conditions like metabolic syndrome, which can further impact energy levels, muscle function, and overall health.
Diagnosing Sarcopenia
Diagnosing sarcopenia involves a comprehensive assessment of muscle mass, strength, and function. Healthcare professionals use various methods to evaluate these parameters and determine the extent of muscle loss.
One common method for diagnosing sarcopenia is measuring muscle mass using imaging techniques such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) or bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA).
In addition to measuring muscle mass, healthcare professionals evaluate muscle strength and physical performance. Tests such as handgrip strength and walking speed are commonly used to assess these aspects. A combination of these assessments helps create a comprehensive picture of your muscle health, aiding in the diagnosis of sarcopenia.
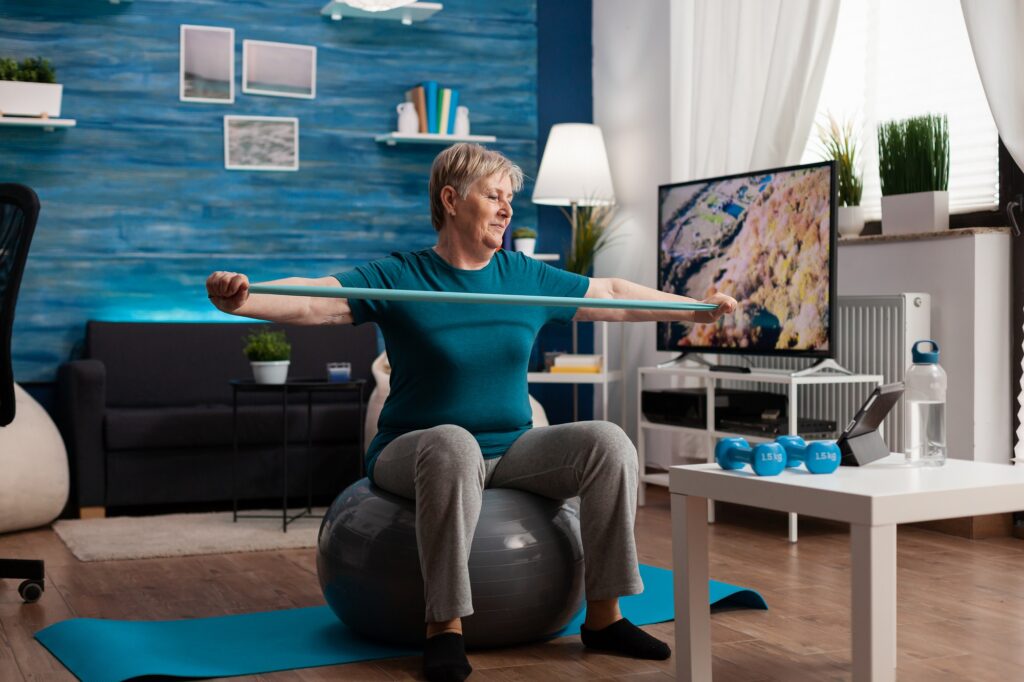
Prevention and Nutrition Strategies for Sarcopenia
Preventing sarcopenia involves maintaining an active lifestyle, eating a balanced diet, and adopting healthy habits. Engaging in regular physical activity supports muscle strength and function as you age.
Nutrition plays a key role in prevention. Consuming adequate protein from sources like lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and nuts provides the building blocks for muscle maintenance. Vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin D and calcium, are essential for muscle function and bone health. These can be obtained through diet and sun exposure.
In addition to exercise and nutrition, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight are important to reduce the risk of sarcopenia and support overall well-being as you age.
Exercises for Sarcopenia
Resistance training is essential to rebuild muscle mass and strength. Incorporate exercises such as weightlifting, resistance bands, squats, and push-ups into your routine. Aerobic activities like walking, cycling, and swimming enhance cardiovascular health and endurance. Flexibility exercises such as stretching and yoga improve joint mobility and reduce stiffness, supporting overall physical function.
Treatment and Role of Healthcare Professionals
Managing sarcopenia requires a comprehensive approach combining lifestyle changes, personalized nutrition, and professional support. Physicians assess your overall health, diagnose sarcopenia, and develop tailored treatment plans.
Registered dietitians provide nutritional guidance, recommend supplements if needed, and help design balanced diets to support muscle repair and growth. Physical therapists create exercise programs focused on improving strength, balance, and mobility, while also offering motivation and supervision. Collaborating with these healthcare professionals ensures your treatment is effective and personalized to your needs, improving muscle health and quality of life.
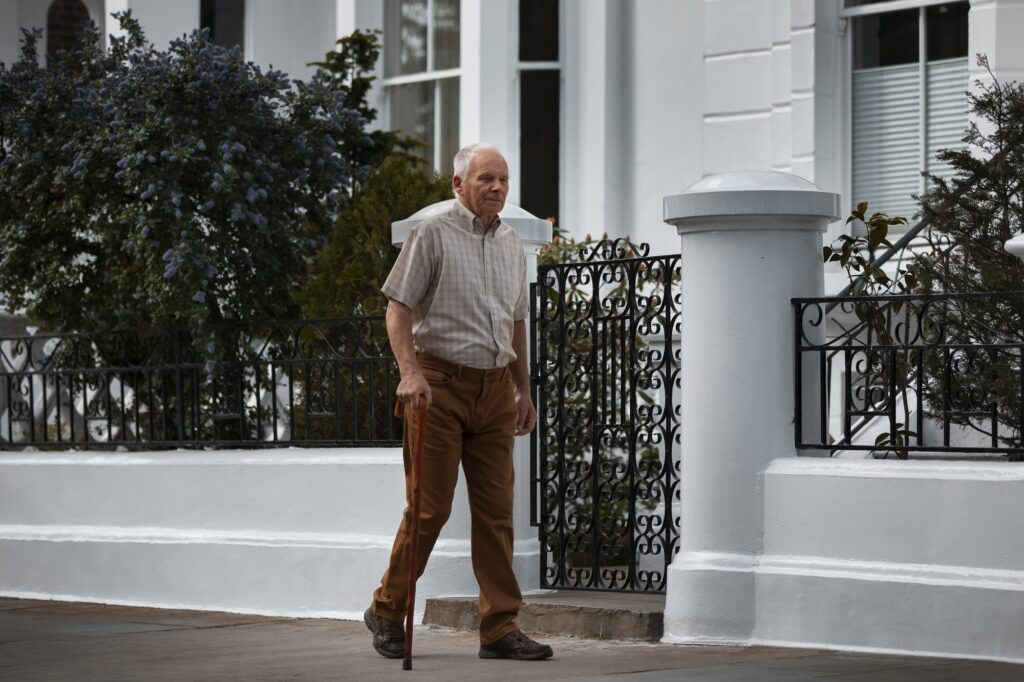

Conclusion
Embracing healthy aging involves recognizing the importance of muscle health and taking proactive steps to prevent and manage sarcopenia. Maintaining an active lifestyle, prioritizing nutrition, and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals are key components of a comprehensive approach to healthy aging.
By taking these steps, you can enhance your quality of life, maintain independence, and reduce the risk of age-related complications. Embrace the opportunity to invest in your health and well-being, and enjoy a fulfilling, active life for years to come.