Dementia
Dementia syndrome takes place due to brain cell damage. These damaged brain cells deteriorate the brain’s ability to link with its various parts. Dementia can also be caused by blood flow hindrance causing hypoxia (low oxygen supply). Brain cell death takes place due to oxygen and nutrient deprivation.
Brain damage will lead to multiple symptoms depending upon the parts which are damaged. Few types of dementia are irreversible and lead to more deterioration over time. However, it can be cured or managed with treatment.
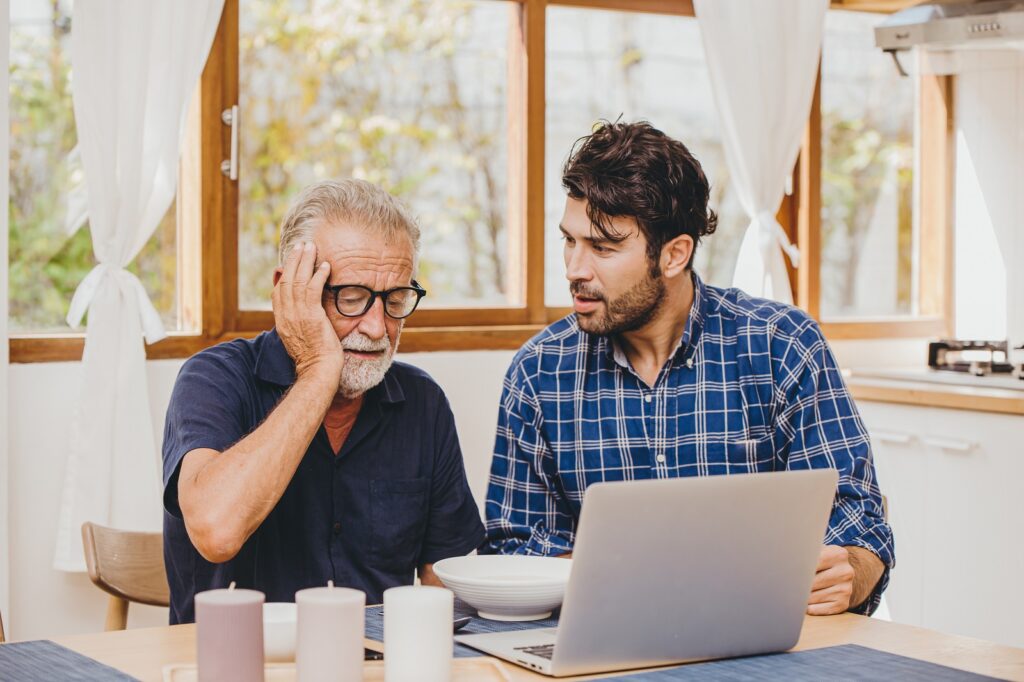

What Is Dementia?
It is a syndrome responsible for cognitive function (capability to regulate thoughts) deterioration. It is generally progressive or chronic in nature. It will lead to a decline in below mentioned two or more functions:
- Reasoning
- Orientation
- Language
- Memory
- Mood
- Coordination
- Behavior
- Learning capacity
Types of Dementia
Dementias are classified into three major groups:
- Primary
Dementia is the main illness in it.
- Secondary
Dementia is caused by another underlying disease or illness
- Reversible dementia-like symptoms
Symptoms resembled dementia but the cause or disease is different.

Primary Dementia
Types of primary dementia are as follows:
Alzheimer’s Disease
It is the most recurrent type of dementia. About 60%-80% of patients diagnosed with dementia are suffering from Alzheimer’s. Its major target is older people of age 85 and above. It is caused by the building up of two abnormal proteins in the brain (amyloid and tau proteins). The communication between nerve cells in the brain became disrupted. It will disrupt the brain cell’s ability to utilize insulin. Progressive damage to the nerve cell took place causing cellular death. So, could be named type3 diabetes. Symptoms of dementia are:
- Short-term memory loss
- Confusion
- Personality changes
- Behavioral changes
- Difficult speech
- Trouble while walking
Vascular Dementia
After Alzheimer’s, it is the most common type of dementia. Strokes or atherosclerosis causes blockage and damage to the blood vessels of the brain leading to vascular dementia. Symptoms might be abrupt or gradual depending upon the type of stroke. Its symptoms are:
- Memory issues
- Confusion
- A problem in concentrating and task completion
High cholesterol levels, high blood pressure, and diabetes are the risk factors of vascular dementia.
Lewy Body Dementia
Lewy bodies, a clump of proteins buildup in the brain’s nerve cells. They will deteriorate the nerve cells leading to dementia. Symptoms are:
- Mobility issues
- Balancing problem
- Sleep pattern changes
- Problem-solving difficult situations
- Visual hallucination
- Delusions
Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD)
The frontal and temporal bones of the brain get damaged due to the development of abnormal proteins in them. Symptoms associated with it are :
- Loss of language skills like understanding, speaking, or memorizing the meaning of common words.
- Social behavioral changes
- Personality changes
- Motor coordination
Mixed Dementia
It occurs in conjunction with other types of dementia. A combination of Alzheimer’s and vascular dementia are mostly seen. People above 80 are mostly suffered from mixed dementia. Symptoms may overlap so difficult to diagnose. Pathological damage is abrupt and of serious nature.
Secondary Dementia
This dementia is an underlying condition due to other diseases. These causes include:
Huntington’s Disease
It is caused by a defective gene that causes the brain’s nerve cells to deteriorate. Symptoms are:
- Movement and body control issues
- Decision-making problems
- Memory trouble
- Personality changes
Parkinson’s Disease
In the advanced stages of Parkinson’s disease, patients would develop dementia. Symptoms include:
- Thinking issues
- Memory problems
- Speech issues
- Hallucination
- Delusions
Creutzfeldt-jakob Disease
The prions, an abnormal protein is the cause of creutzfeldt-jakob disease. It is a rare condition affecting brain nerve cells. Prions start accumulating in the brain causing brain cell death. Its symptoms are:
- Agitation
- Depression
- Judgment issues
- Communication and thinking problems
- Memory-related issue
- Behavioral changes
Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome
A severe vitamin B1 (thiamine) deficiency causes this syndrome. It causes bleeding in the memory-related areas of the brain. It may occur due to alcohol use disorder, chronic infection, or malnutrition. Symptoms are:
- Double vision
- Loss of muscle coordination
- Difficult to learn new skills
- Memory issues
Traumatic Brain Injury
Repeated hits to the head may lead to trauma. It’s most common in boxers, footballers, soldiers, or accidental cases. its symptoms may take years to appear including:
- Memory loss
- Mood changes
- Behavioral issues
- Headache
- Slurred speech
Dementia Due To Reversible Sources
A few diseases do have dementia-like symptoms but are reversible. These are mentioned below:
Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH)
Cerebrospinal fluid building up in the brain’s ventricles gave rise to Normal pressure hydrocephalus. This fluid has harmful effects on the brain. It may lead to brain injury, bleeding, infections, etc. symptoms of NPH are:
- Poor balance
- Loss of bladder control
- Focussing issues
- Mood swings
- Memory loss
The neurosurgeon would recommend a shunt placement in the brain for draining excessive fluid.
Vitamin Deficiency
A deficiency of vitamin B1, B6, B12, copper, and vitamin E may lead to dementia-like symptoms.
Infections
These infections include:
- Lyme disease
- Syphilis
- HIV infection
- Covid-19
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- CNS infections (bacteria, fungus, or parasites)
Metabolic and Endocrine Condition:
These are
- Addison’s disease
- Cushing disease
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)
- Mercury or arsenic poisoning
- Hypercalcemia
- Liver cirrhosis
- Thyroid issues
Medicinal Side Effects
Few medicines have dementia-like symptoms. These are
- Sleeping pills
- Anti-anxiety medicines
- Anti-seizure drugs
- Anti-depressants
- Antiparkinsons drugs
- Nonbenzodiazepine sedatives
- Narcotic pain relievers
- Statins
Miscellaneous Causes
These includes
- Brain tumors
- Subdural hematomas (internal bleeding in the brain)
Symptoms of Dementia
Dementia-related symptoms may vary depending upon their cause but the most common signs are mentioned below:
Cognitive Changes
- Memory loss remains unnoticed by the sufferers.
- Difficult to communicate and find words
- Visual and spacial abilities affected
- Facing difficulty in reasoning and problem solving
- Difficult to handle complex tasks
- Managemental or planning problems
- Coordination and motor functions impairment
- Disorientation, Confusion

Psychological Changes
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Personality changes
- Agitation
- Paranoia
- Inappropriate behavior
- Hallucinations
Complications of Dementia
Complications associated with dementia are as follows:
- Bedsores
- Bone fractures
- Injuries
- Malnutrition or dehydration
- Strokes
- Kidney failure
- Heart attacks
- Pneumonia or aspiration pneumonia
- Sepsis (infections)
Dementia Diagnosis
It is a very difficult task to differentiate dementia from other diseases. Many diseases share similar symptoms with dementia. A neurologist will ask you the following questions:
- Duration of the onset of the symptoms
- Medical history
- Current medication
- Family history
Then he will suggest you few tests for confirmatory diagnosis. These are labs, neurocognitive tests, and imaging tests.
Laboratory Tests
These are performed to differentiate dementia from other diseases such as., inflammation, infections, underactive thyroid, and vitamin deficiency (thiamin). Cerebrospinal fluid testing is also recommended to diagnose neurodegenerative or autoimmune disorders.
Imaging Tests
These include brain image testing:
Computerized Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
Provides evidence for stroke, tumors, bleeding, and fluids in the brain.
FDG-PET Scan
This test determines the rate of glucose absorption by the brain tissues. It will judge the cognitive decline pattern and brain functioning.
Neurocognitive Testing
This test will evaluate your mental abilities through written and computerized tests. They will evaluate your following senses:
- Judgment
- Memory
- Planning
- Problem-solving reasoning
- Language
Psychiatric Evaluation
A psychiatrist will examine for the signs of anxiety, depression, mood swings, or other mental health problems leading to memory loss.
How To Treat Dementia?
FDA approved drugs for Alzeihmers are:
- Cholinesterase inhibitors
- Donepezil
- Rivastigmine
- Galantamine
- NMDA receptor antagonist
- Memantine
- Anti-amyloid antibody
- Aducanumab
These drugs could restrict dementia progression but can only slow it down.
Prevention
We can’t prevent dementia but living a healthy and active life may reduce its risk factors. Following preventive measures should be adopted:
- Normal blood pressure
- Maintain normal insulin levels
- Weightloss to prevent obesity
- Quit smoking
- Ketogenic diet plan
- Exercise
- Healthy brain activities to enhance cognitive functioning
- Social activeness
Dr.Waseem’s Way Of Treating Dementia
Dr.Waseem being a dietitian and fitness trainer treat his patients through dietary and lifestyle modifications. Medicines do have many side effects so should be avoided as much as possible. He is a firm believer in ‘ilaj bil ghiza’. The following paraments have been suggested by Dr.Waseem to his patients for brain and body fitness:
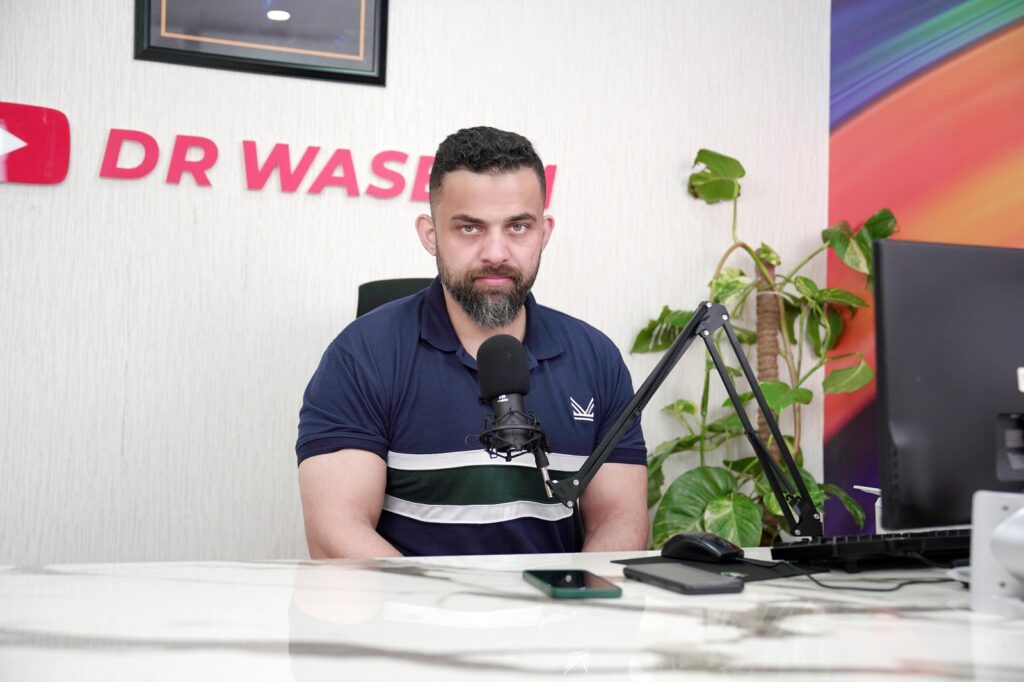

- Intermittent fasting lowers insulin levels in the body. Alzheimer’s is caused by insulin resistance development in the brain so fasting is beneficial to treat it.
- Moderate exercise as lean muscles enhances insulin receptors. Exercise helps to regulate enough blood flow and supports new brain cell growth and survival rates. This delays or prevents the chances of having dementia.
- A therapeutic ketogenic diet having high fat and low carb is very beneficial for treating dementia. It includes vegetables (cauliflower, cucumber), nuts, and keto-friendly fruits such as berries. Fats from olive oil, cream, butter, cheese, and coconut oil. Proteins from boiled eggs, beef, mutton, chicken, or flex seeds.
- Healthy brain exercises like solving puzzles, playing games, etc.
- Reduce weight for reducing the risks of cardiovascular disorders or diabetes.
- Avoid stress
- Proper sleep pattern
- Supplements having multivitamins (especially thiamine and vitamin D) should be taken on a regular basis
- Do consult a psychiatrist if facing anxiety, depression, or other psychological problems
- Regular follow-ups with your healthcare practitioner.
Unfortunately, the most common type of dementia i.e Alzheimers’ is untreatable but could be managed or slowed down by adopting the above-mentioned parameters.

An Ultimate Solution to your Fitness & Health Problems
The Ginnastic Health Center In Islamabad is a state-of-the-art clinic with one of its kind modern health services in Islamabad that is offering a complete range of treatments for a variety of health care concerns including chronic illnesses and pain management.