Fatty Liver
Fatty liver is also named hepatic steatosis. It is a condition in which fat gets deposited in the liver. Slight deposition of fat on the liver doesn’t affect its functionality, however, the excessive deposition could have detrimental effects on one’s body.
It may lead to liver inflammation causing cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease having scarring on it.

The liver is the largest internal organ of the human body. It is situated below the rib cage in the abdominal cavity on the right side. It performs over 500 functions and plays a vital role in blood detoxification. A few of its functions are mentioned below.
- Amino acid regulation
- Production of Albumin
- Bile production for absorption and digestion in the small intestine
- Blood filtration from toxins or other detrimental substances
- Blood clotting regulation
- Defensive mechanism from bacterial infections
- Processes glucose by storing it as glycogen
- Stores minerals and vitamins e.g., Vitamin A,D,E,K,iron,copper etc.
Types of Fatty Liver
Alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD)
Alcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with alcoholic intake. Alcohol could be broken down by the liver but the end products of this reaction would have detrimental effects on the body.
They would damage hepatic cells, impair defense mechanisms and enhance inflammatory processes. With the passage of time increasing alcoholic intake promotes liver damage resulting in liver cirrhosis and alcoholic hepatitis.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD):
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is not linked with alcoholic intake. NAFLD is further divided into two types;
- In uncomplicated non-alcoholic fatty liver cells remain uninflamed and don’t let liver function impairment. No liver complications have been noticed in it.
- In non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, hepatic cells get inflamed and cause fibrosis, scarring, and other medical complications. It may lead to liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma).
Causes of Fatty Liver
Metabolic syndrome
The most recurrent diseases associated with fatty liver are Wilson Disease, Alpha-I antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), and hereditary hemochromatosis. These complaints ended up in liver cancer or cirrhosis.
Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance would lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Genetically originated insulin resistance would elevate serum triglycerides.
Type 2 Diabetes
An increase in blood glucose level in the case of diabetes type 2 proves to be a substrate for triglyceride elevation. And reduces VLDL. This will lead to fat accumulation in the liver.
Obesity
Hepatic steatosis is strongly linked with obesity. An overweight person will always be at risk of developing fatty liver.
High triglycerides in the blood
Elevated levels of triglycerides in the blood are indicative of high-fat content in blood, meanwhile, it’s also a red signal for fatty liver.
Low HDL or high LDL
Normal cholesterol levels are an indication of a healthy person but if their range values become altered it may lead to a few serious complications.
Pregnancy
In pregnancy, acute fatty liver is a serious medical condition and should be treated immediately.
Hepatitis C
Patients with hepatitis C are at risk of developing fatty liver leading to cirrhosis.
Polycystic Ovary
Females having PCOS have elevated liver enzymes. The cause of PCOs is hormonal imbalance displaying insulin resistance leading to hepatitis.
Genetic
Genetic variation of the PNPLA3 gene leads to fatty liver.
Medicinal side effects
Side effects of tamoxifen, total parenteral nutrition, steroids, griseofulvin, valproate, methotrexate, and amiodarone resulted in fatty liver.
Toxins exposure
Common toxins causing fatty liver are polychlorinated biphenyls or vinyl chloride. chloride.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver
Fatty liver is a silent disease showing few unnoticeable symptoms. One could feel tiredness, restlessness, or pain on the right stomach side. Its symptomatic progression is at four stages:
Simple fatty liver
Fat is deposited in the liver but it doesn’t have detrimental effects as its non-progressive.
Steatohepatitis
At this stage, fat deposition is leading to hepatitis i.e., inflammation of hepatic cells.
Fibrosis
The liver would undergo a scarring process if persistent inflammation is there. Although liver functioning remained uninterrupted.
Cirrhosis
An irreversible and acute stage that will impair liver functioning is cirrhosis. Symptoms associated with cirrhosis are as follows:
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Inappetance
- Itchy skin
- Abdominal cramps
- Jaundice (yellowness of skin and eyes)
- Bleeding disorder
- Edema (swelling) of limbs
- Ascites (excessive fluid accumulation in the abdomen)
- Web-like blood vessels under the skin
- Enlarged breast in men
- Nervousness
- Pale stool
- Dark colored urine
Fatty liver is a life-threatening disease in advanced stages so, should be controlled at an early stage.
Diagnosis of Fatty Liver
Fatty liver is asymptomatic in the early stages so it’s very difficult to diagnose it at that time. Healthcare practitioners would use the following tools for diagnosis:
Medical record
Examiner would ask the patient about his alcohol intake, eating habits, medicines in use, or previous medical complaints like hepatitis C.
Physical examination
The practitioner will examine a few parameters including., weight, age, and paleness of skin or gums.
Blood tests
It will detect levels of hepatic enzymes like aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and Alanine aminotransferase (ALT). Their high levels would indicate liver malfunctioning. Lipid profiles will aid them to detect cholesterol, LDL, or HDL levels.
Imaging tests
These tests include CT scans (Computerized Tomography), Ultrasound, and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) to aid in imaging fat deposition on the liver.
Liver biopsy
The biopsy is performed in case of cirrhosis or other complications associated with it. Tissue culture is obtained from the surface of the liver and sent to the laboratory for further diagnosis. Inflamed hepatic cells could be detected by following this protocol.
Risk factors
Risk factors for insulin resistance are obesity,high blood pressure,triglycerides or major depression syndromes. The elevated blood pressure and triglycerides are the main cause of cardio-vascular disorders leading to heart stroke. Regular follow up is mandatory to avoid detrimental effects.
Treatment of Fatty Liver
Weight reduction
A key factor to control fatty liver is to reduce weight. An obese person will have more chances of developing inflammation or fibrosis.
Medicine withdrawal
The practitioner might ask the patient to withdraw his previous medication if they are affecting his liver. Instead, he will prescribe you a liver-friendly medicine for the same cause.
Avoiding alcoholic intake
The crucial step in treating the disease is to cut off your alcohol intake. Either you have to join an alcohol recovery program or have to visit a therapist to meet the cause.
Medicine
No medicine is treatable for fatty liver. But researchers discovered vitamin E or diabetes controlling medicine helps overcome the disease.
Liver transplant
Cirrhosis is an irreversible problem ultimately resulting in liver failure. so, at this stage, the only solution is to transplant the liver.
Lifestyle alterations
At the initial stage fatty liver could be treated by adopting the following lifestyle changes:
Diet
Following a plan to have a nutritious diet in it like increasing fruits, vegetables, and wholegrains intake. Reduces processed food, salt, and sugar intake.
Vaccination
Vaccination against hepatitis A and B could save the liver from hepatitis leading to cirrhosis. A shot against flu and pneumococcal disease could also be beneficial for it.
Exercise
Regular exercise ends up reducing weight as well as fat in the liver.
Medicine / Supplement intake
Avoid any medicine or supplement without a doctor’s prescription. Certain medicines are liver damage, so should be avoided in such cases.
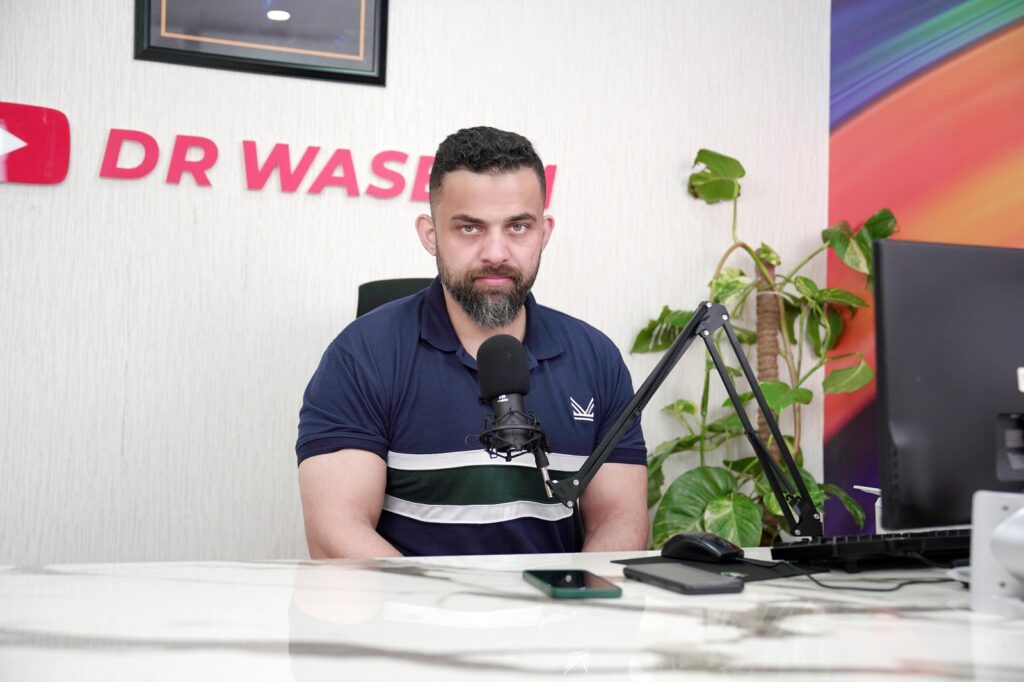
Dr. Waseem’s Treatment
Dr.Waseem has a versatile way of treating a disease. After a diagnosis of any medical condition, he would prefer to treat it naturally, without prescribing a drug.
He believes that therapeutic drugs do have many side effects, so should be avoided as much as possible. Although there comes a situation when one has to start his medical course.


An Ultimate Solution to your Fitness & Health Problems
The Ginnastic Health Center In Islamabad is a state-of-the-art clinic with one of its kind modern health services in Islamabad that is offering a complete range of treatments for a variety of health care concerns including chronic illnesses and pain management.